Completed funded project
Motivation
The development of new products is subject to increasing international competition. Faster and more cost-effective developments offer an important competitive advantage. Computer-based methods make a significant contribution to this. Shorter development cycles are particularly important in the field of thermal process technology, because rising energy prices and higher environmental requirements require the rapid implementation of new thermal processes and industrial furnaces.
Objective
The DiMaWert project aimed to develop new methods and implement existing methods with which products can be planned and brought to market more quickly. The focus was on sustainable industrial thermal processes. New high-temperature materials and components, improved process parameters, high-temperature measurement methods and sensors as well as so-called digital furnace twins were to be developed for industrial thermal processes. The digital furnace twins simulate the thermal process in the computer so realistically that improved thermal processes can be derived from them.
Results
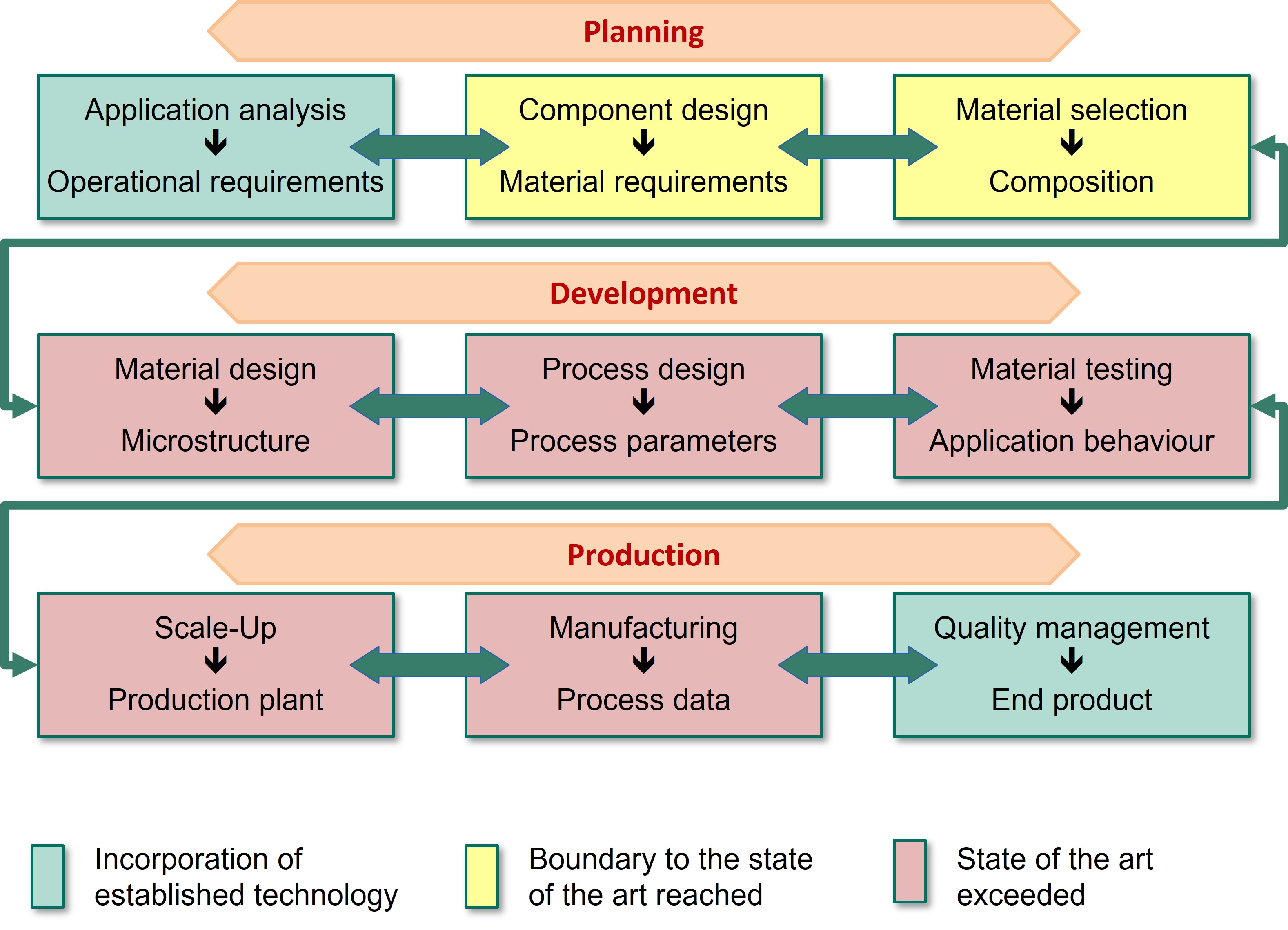
- In the DiMaWert project, ICME (Integrated Computational Materials Engineering) was used to efficiently combine the various stages of product development. The state of the art was significantly expanded in many stages of the development chain (Fig. 1).
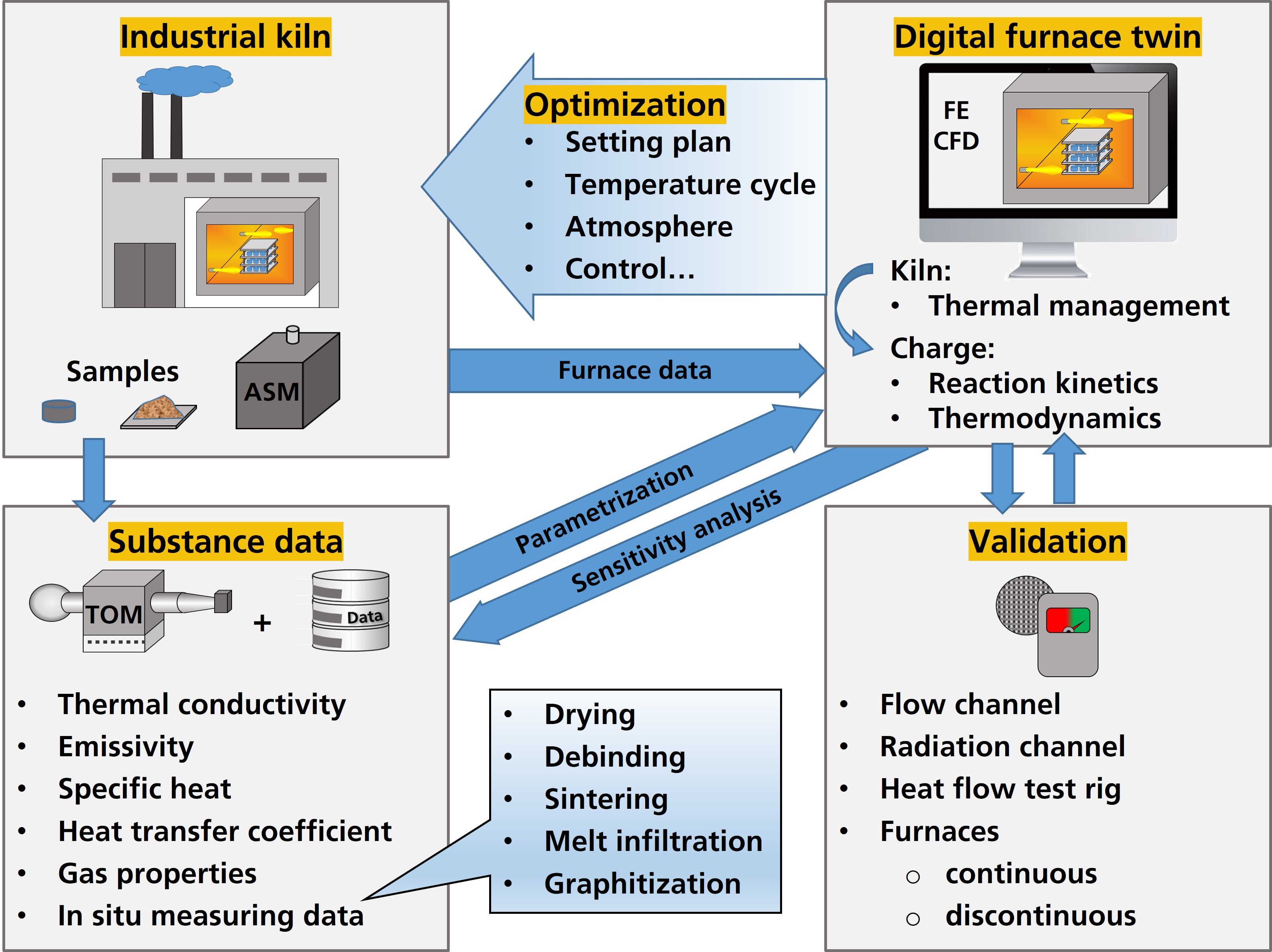
- A model based on high-temperature material data was developed and successfully validated for the digital furnace twin. The simulation combines the heat transport in the furnaces with the response behavior of the material to be heated. It can be used for a variety of thermal processes (Fig. 2).
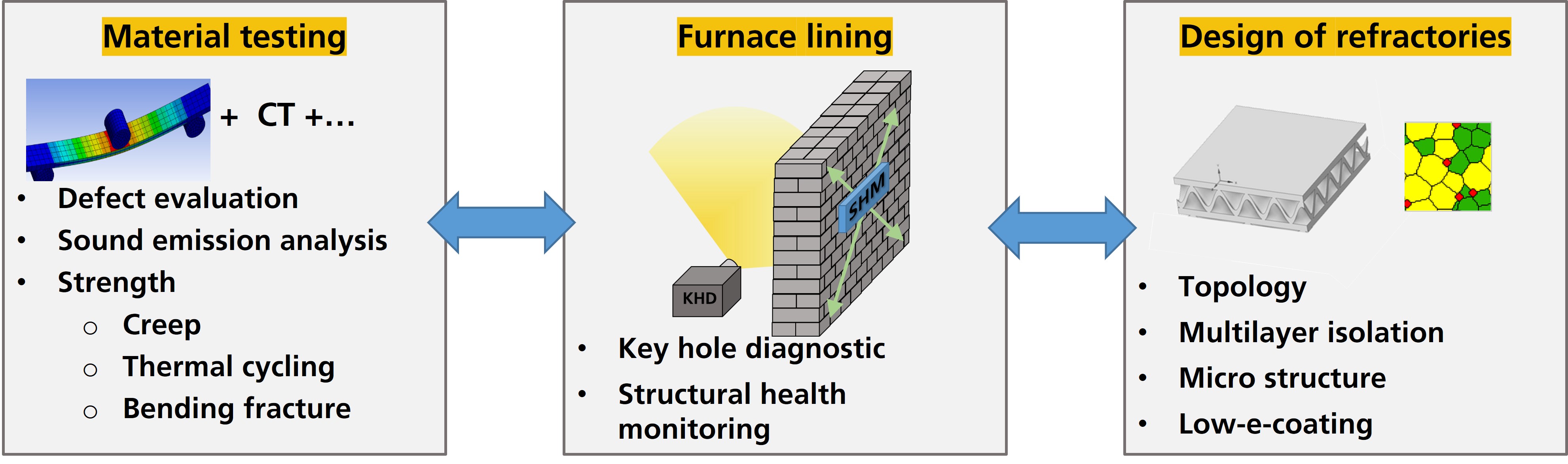
- New characterization methods have been developed for refractory materials. For example, the ageing behavior during thermocycling can be investigated in situ using acoustic emission analyses. Insights into fracture mechanical behavior can be derived from microstructure investigations. Autonomous sensor modules can be used to monitor the furnace lining (Fig. 3).
Project structure
The DiMaWert project was organized in eight networked sub-projects:
- DigiTherm: Model Integration
- DigiTherm: Virtual Construction
- DigiTherm: Process Development
- DigiTherm: Life Cycle Assessment
- DigiSens: Optical Sensor Technology
- DigiSens: Structural Health Monitoring
- DigiRaum: Autonomous Sensor Module
- DigiRaum: AI Algorithms
 Fraunhofer ISC, Center for High Temperature Materials and Design HTL, Bayreuth
Fraunhofer ISC, Center for High Temperature Materials and Design HTL, Bayreuth