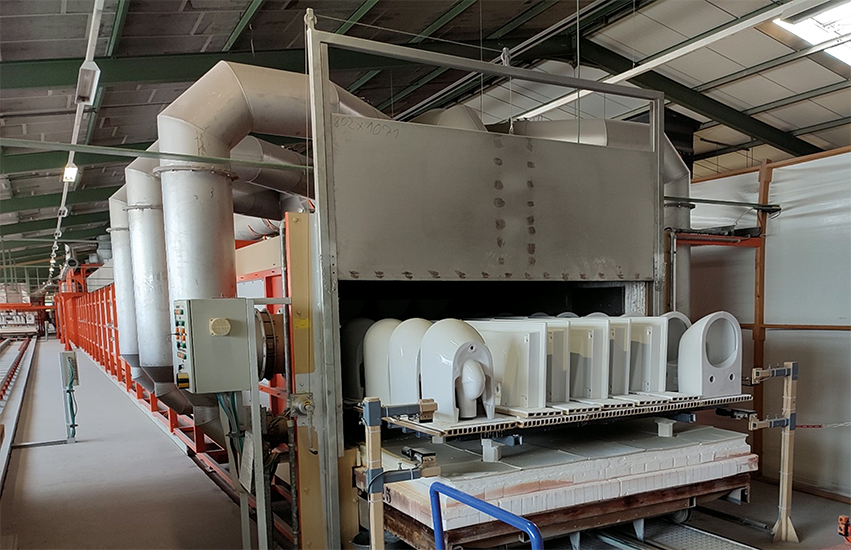
Completed Funded Projects
Motivation
The need to reduce CO2 emissions and the increasingly fluctuating energy supply from regenerative sources are a challenge both for industrial furnace construction and for operators of high-temperature processes. Networked computer models and precise measurement data are indispensable as a basis for model calculations in order to be able to guarantee optimum energy efficiency and consistently high product quality, not only in the design of new furnace systems but also in the control and monitoring of production processes in furnaces. The project aims to develop appropriate digital tools for the future needs of furnace manufacturers and users.
Objective
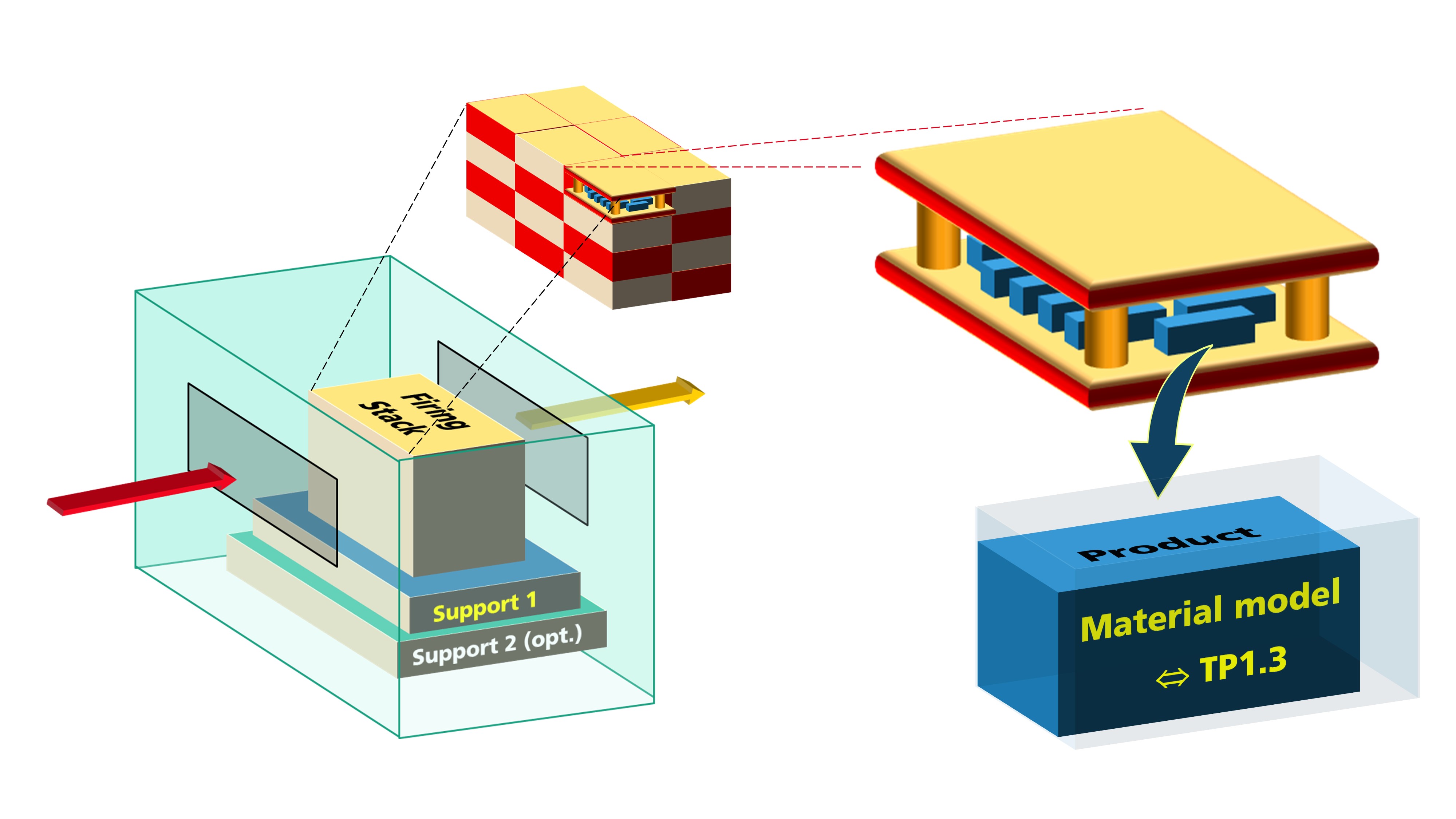
The aim of this sub-project was to develop concepts and methods that enable the virtual development of thermal process plants with the aid of digital furnace twins. In the field of furnace simulation, this includes in particular the selection and validation of submodels for the efficient modeling of large industrial furnaces and the coupling of material and thermal models on the various scales under consideration. Equally important are methods for the procurement and quality-assured internal provision of precise material data from databases, literature and our own measurements.
Results
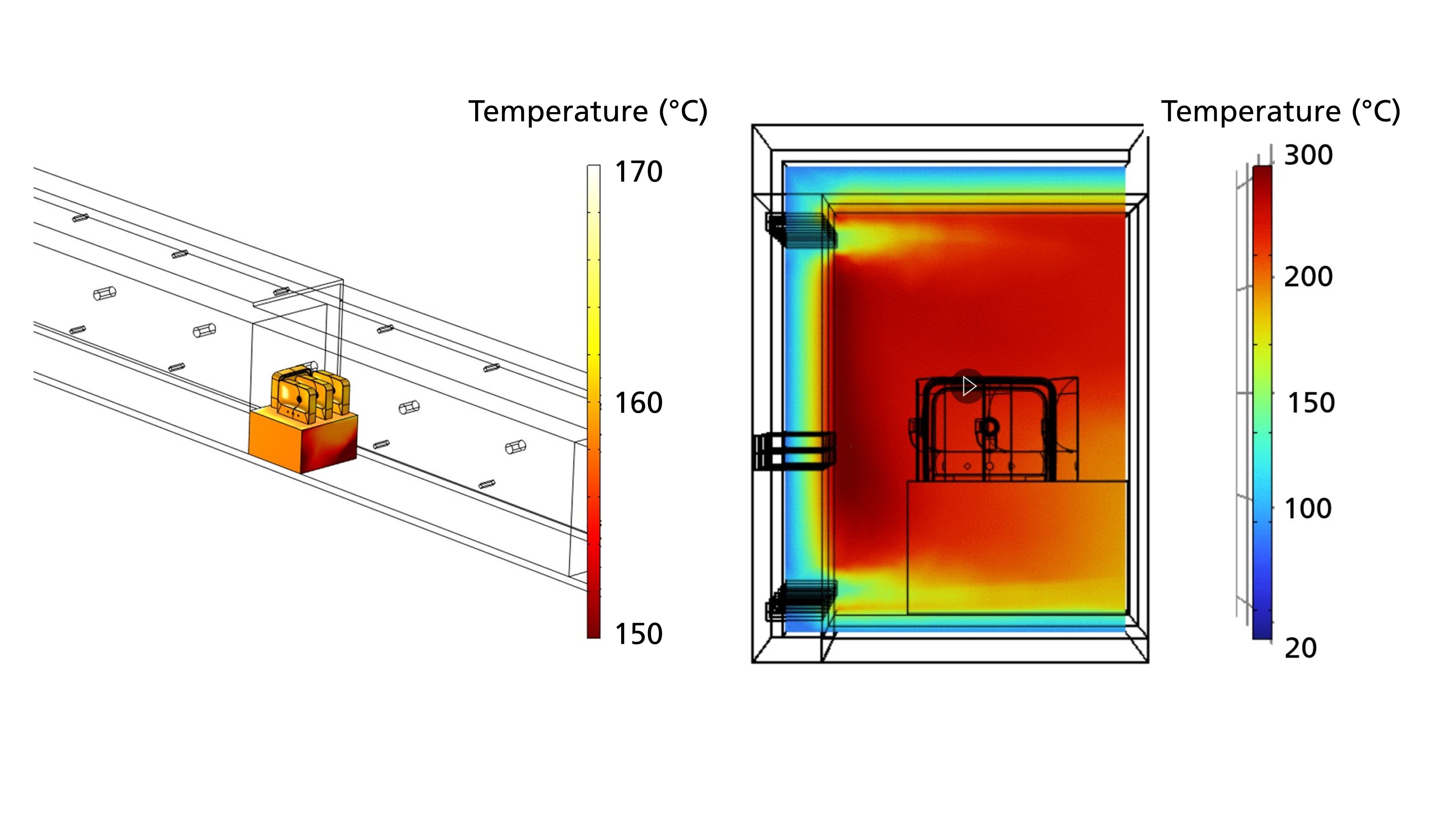
- Selection and procurement of suitable databases
- Scripts for material data search and parameterization
- Development of methods for topology optimization of furnace components:
- App for the design of kiln insulation
- Methods for the topology-optimized design of kiln furniture
- Development of a submodel concept for large industrial kilns
- Selection, testing and experimental validation of important simulation methods (FE, CFD)
- Networking, further development and supplementation of the simulation methods available at the HTL in the sense of ICME (Integrated Computational Materials Engineering)
 Fraunhofer ISC, Center for High Temperature Materials and Design HTL, Bayreuth
Fraunhofer ISC, Center for High Temperature Materials and Design HTL, Bayreuth
