At Fraunhofer Center HTL, numerous AI algorithms are used for material and process development. The HTL has powerful hardware and the ability to provide input data through various measurement methods and databases to validate models. The AI methods are selected for specific tasks. In addition to machine learning, classical methods such as finite elements (FE) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) are also used.
AI Algorithms
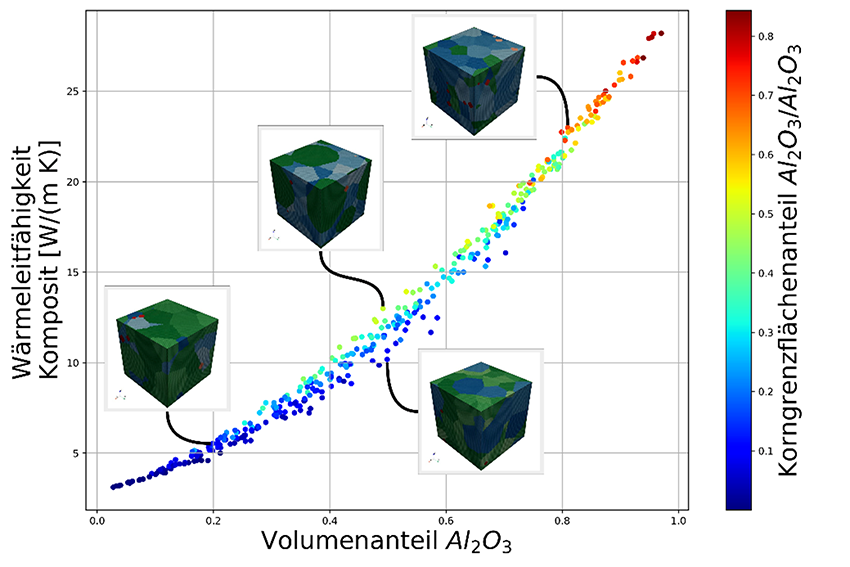
By using AI, manufacturers can better understand and improve the properties of materials and products. AI-supported simulation-based analysis can, for example, be used to investigate and optimize the effects of different material components and process parameters on product properties.
The HTL has years of experience in the field of microstructure-property simulation for ceramic materials. With AI-based models, it is possible to predict achievable material properties based on the microstructure with high accuracy.
The developed microstructure models are provided as apps, enabling the user to calculate suitable compositions to achieve desired material properties. This not only supports product development but also reduces the number of prototypes and significantly reduces the time from the initial product idea to sales.
AI can be used in the ceramics industry to optimize production processes and achieve higher efficiency. For example, the furnace temperature can be automatically monitored and controlled to achieve optimal strength and density of the products, or to minimize energy consumption while maintaining product quality.
At the HTL, AI algorithms are used in the creation of digital twins of furnaces. A digital twin is a virtual version of a real furnace based on data from sensors and other sources. With a digital twin, various scenarios can be simulated and optimized to improve oven performance and minimize downtime.
AI algorithms are used in the creation of the digital twin of the furnace, such as for automated data analysis of measurement data from a real furnace, based on which the digital twin is created and validated. However, the creation of a digital twin based on a finite element (FE) or computational fluid dynamics (CFD) model of the furnace usually involves a large amount of computation, which limits real-time capability.
An extension is the AI-based digital twin of the furnace, which makes it possible to monitor thermal processes in real-time. This monitoring can improve reaction time to unforeseen events. To achieve this, an AI model is trained on the simulation results of the classical digital twin of the furnace and then used for prediction.
Alternatively, AI models can also be trained directly on historical data from the furnace to make predictions about future performance. By analyzing correlations in the furnace's performance data, patterns can be identified, and potential failures can be detected early in the production process.
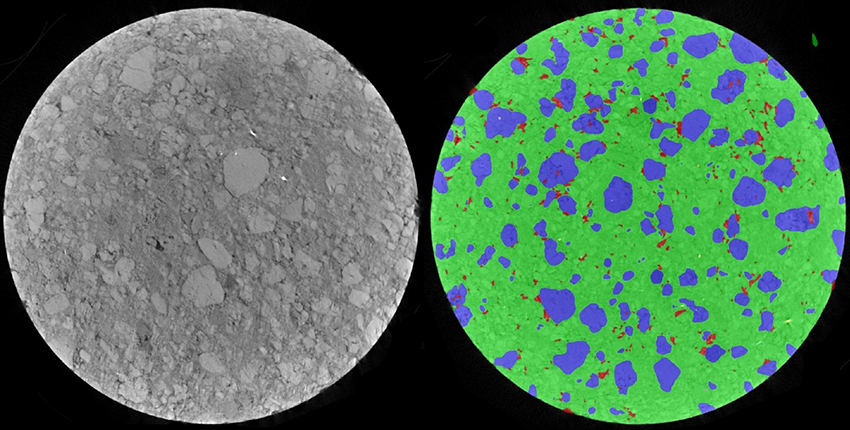
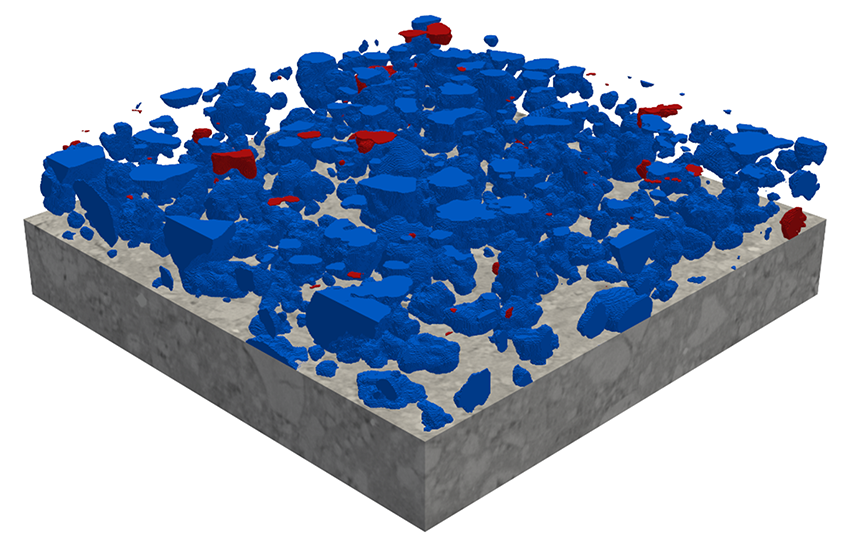
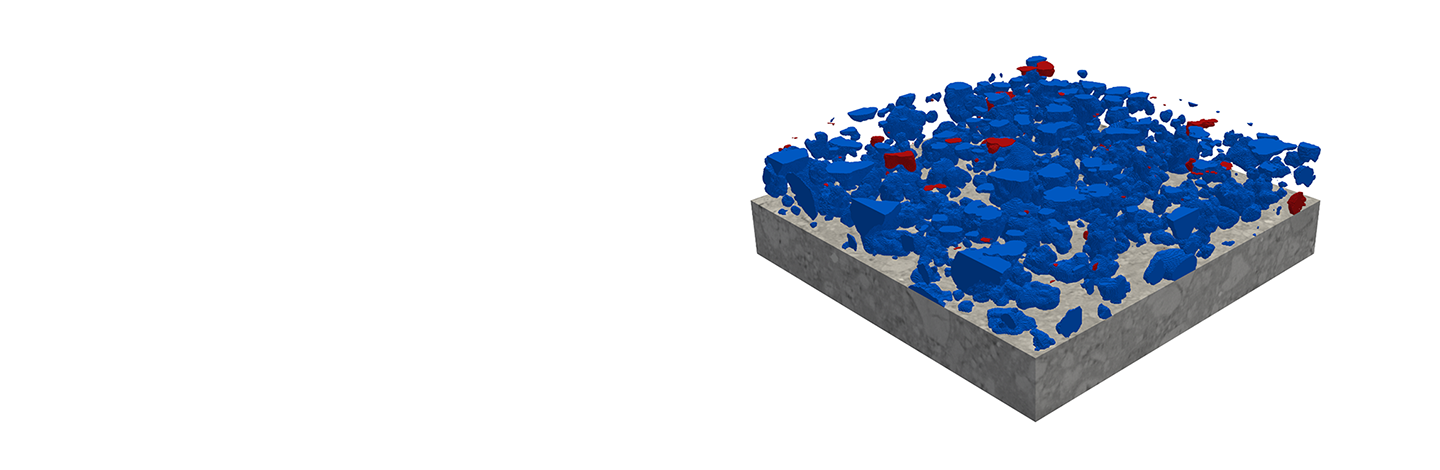
AI methods are used for automated quality control by analyzing image data of products to detect defects and deviations. Two different types of image data are used in quality control: 2D and 3D image data.
2D image data is typically used for inspecting surfaces and cross sections of components. Images of the products are captured in high resolution and then analyzed by AI algorithms. These algorithms can use pattern recognition techniques to detect, for example, cracks, color deviations, unevenness or other deviations on the surface of the products and predict their impact on the life of the component. The use of 2D image data for quality control offers the advantage that it is relatively easy and cost-effective to capture and process.
In contrast, in 3D quality control, the spatial properties of products are analyzed by creating high-resolution 3D scans and evaluating them using AI algorithms. The use of 3D scans allows manufacturers to obtain detailed information about the shape and structure of products, including the inner and outer areas. This enables precise measurement of dimensions and tolerances as well as detection of defects such as cracks, cavities, or other failures that may not be detectable in 2D images.
Service Offering:
- Selection of suitable AI methods for customer-specific questions
- Creation of apps for material and process optimization
- Creation of AI-based digital oven twins
- AI-based analysis of 2D images (light microscopy, scanning electron microscopy) and 3D images (computed tomography) of microstructure and component on different size scales
 Fraunhofer ISC, Center for High Temperature Materials and Design HTL, Bayreuth
Fraunhofer ISC, Center for High Temperature Materials and Design HTL, Bayreuth