Completed funded project
Motivation
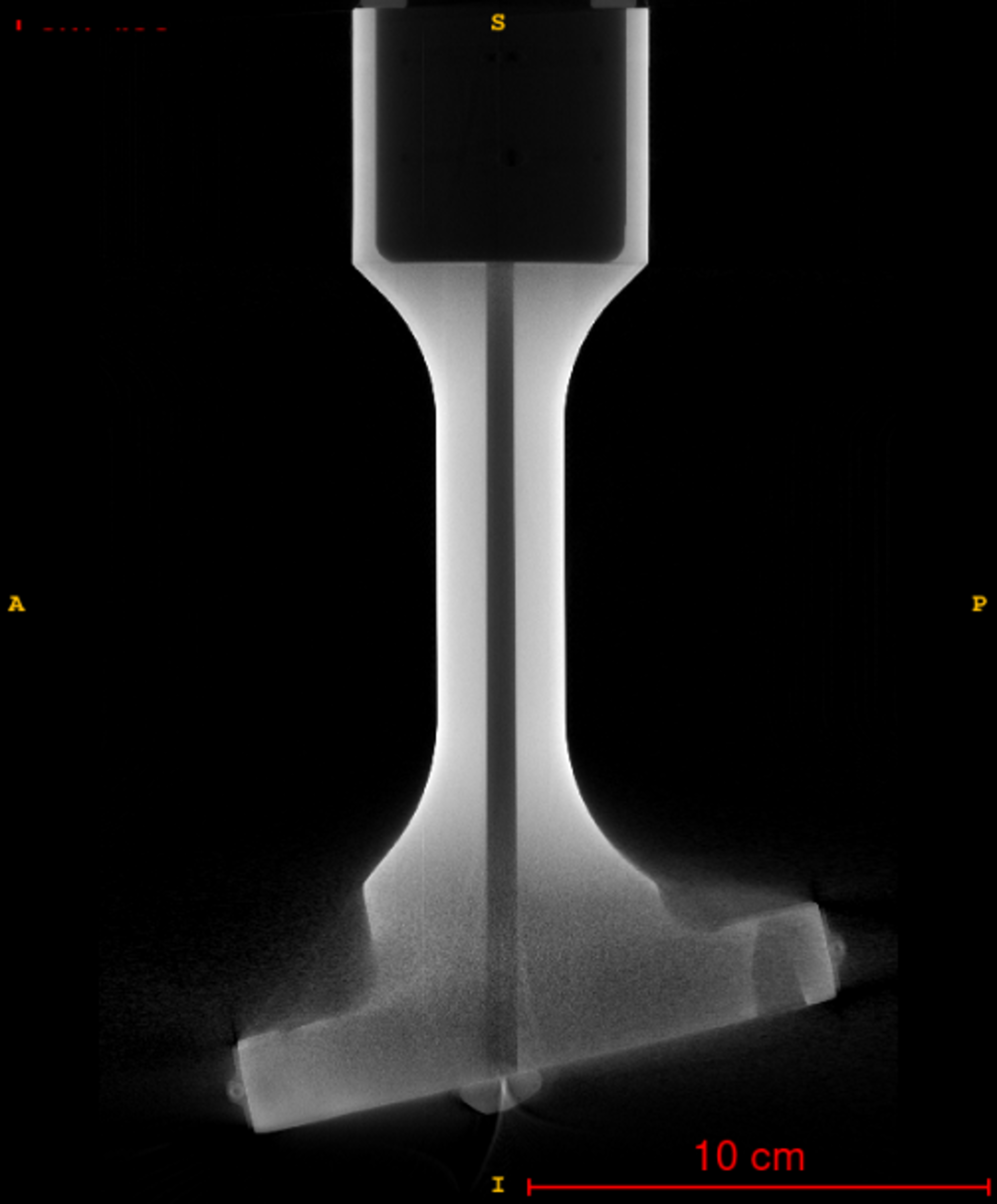
In aerospace components, reliability regarding mechanical failures is of particular importance. This is especially true for ceramic components due to their brittleness, as even a single defect at a critical location can lead to crack formation and catastrophic failure. Currently, extensive stress tests are conducted that exceed the predicted operational limits. This method is not only time-consuming and costly but often induces undesirable stresses and additional risks.
Therefore, there is a strong interest in developing non-destructive testing methods that offer the same reliability but with less effort and time.
Objective
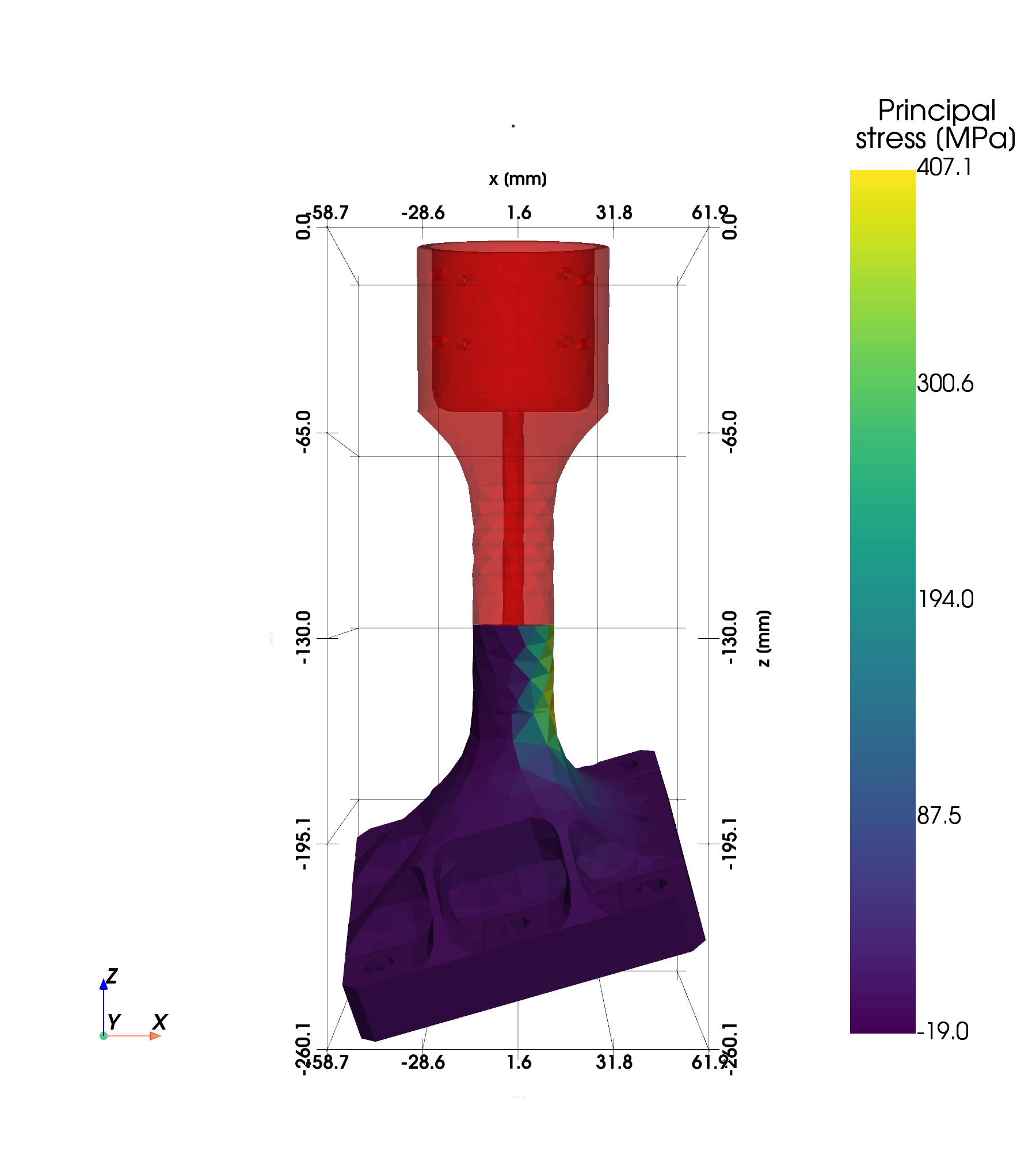
The aim of the project was to develop an efficient and reliable non-destructive testing technique for ceramic materials in aerospace applications. This was to be achieved by combining X-ray computed tomography (CT) imaging with artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms for defect detection and finite element analysis to reliably identify defects and assess their criticality. The technology should be suitable for all space-relevant ceramic materials and also transferable to general material testing.
Results
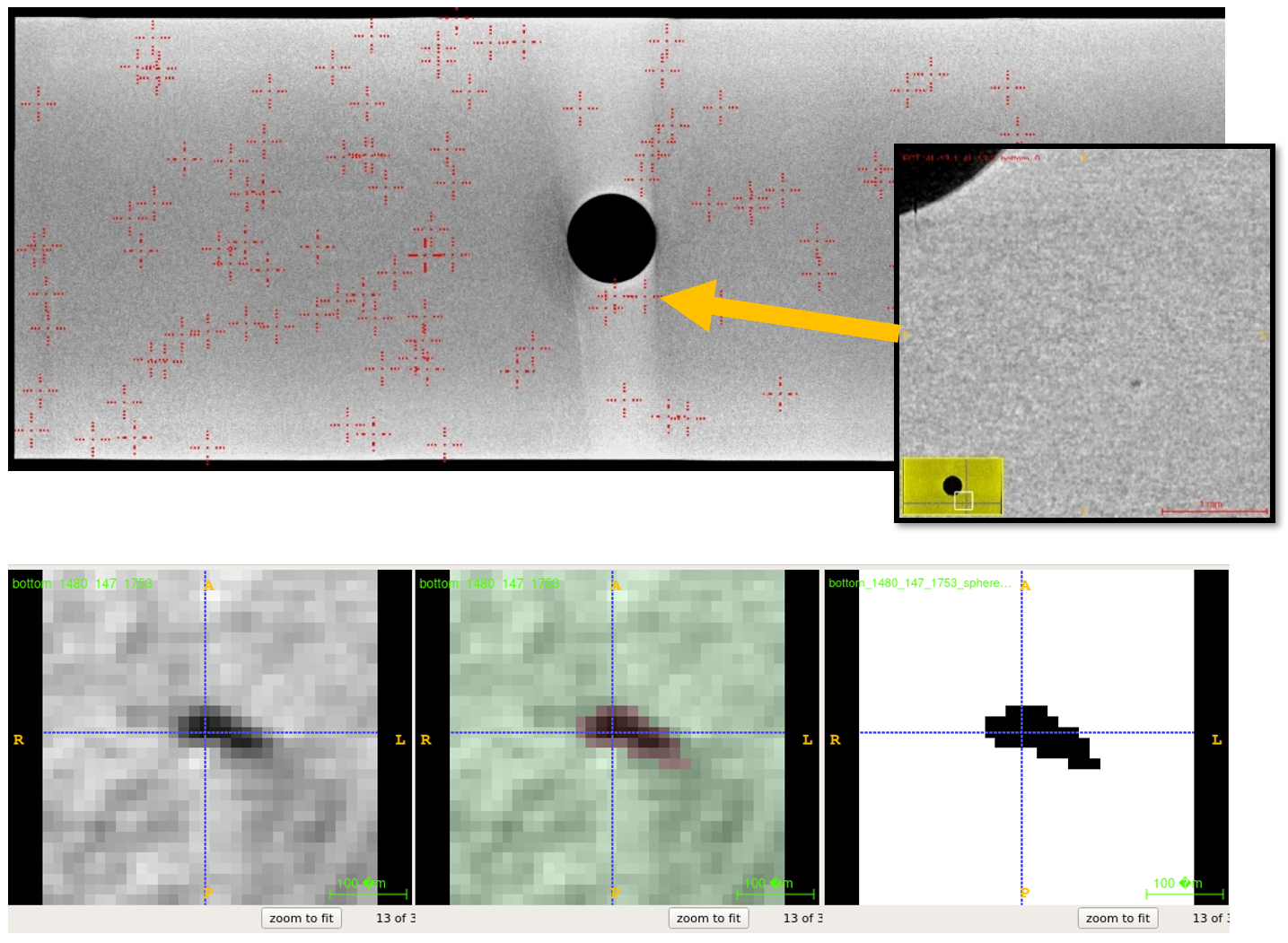
- Powerful AI-based Algorithm for Defect Segmentation: High accuracy (approx. 93%) in pore detection; identification of additional defects that are often overlooked by humans.
- Integration with Finite Element Analysis: Combines defect information with simulated loads to assess defect criticality.
- Adaptive Scanning Procedure: Iterative CT scans with varying resolutions lead to reduced scan times.
- Time Efficiency: Automated defect segmentation and adaptive scanning save significant time compared to classical methods.
- Demonstration of Developed Methodology: Successfully applied to an exemplary ceramic component used in aerospace.
Projekt data
| Project Duration | 07/01/2023 - 06/30/2024 |
| Sponsor | General Support Technologiy Programme (GSTP) ESA |
| Project partner | European Space Agency (ESA) |
| Project lead at HTL | Dr. Simon Pirkelmann |
| Project coordination | PD Dr. Gerhard Seifert |
 Fraunhofer ISC, Center for High Temperature Materials and Design HTL, Bayreuth
Fraunhofer ISC, Center for High Temperature Materials and Design HTL, Bayreuth