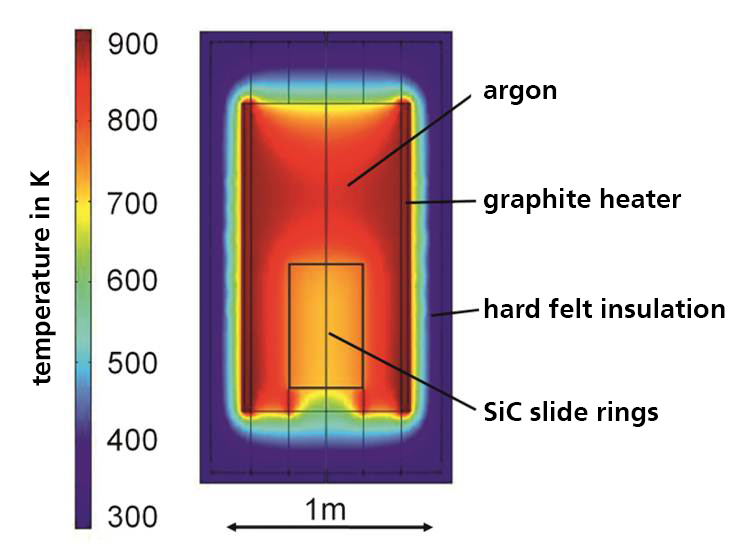
Motivation
The energy efficiency of thermoprocessing plants depends in a complex way on their design, the materials used, the arrangement of the heat treatment material and the process parameters of the heat treatment. The understanding of the interactions between the influencing variables is insufficient. An experimental optimisation of energy efficiency is therefore very costly.
Conversely, FE methods are available with which heat transport phenomena can be calculated taking thermal radiation, convection and conduction into account.
 Fraunhofer ISC, Center for High Temperature Materials and Design HTL, Bayreuth
Fraunhofer ISC, Center for High Temperature Materials and Design HTL, Bayreuth