Motivation
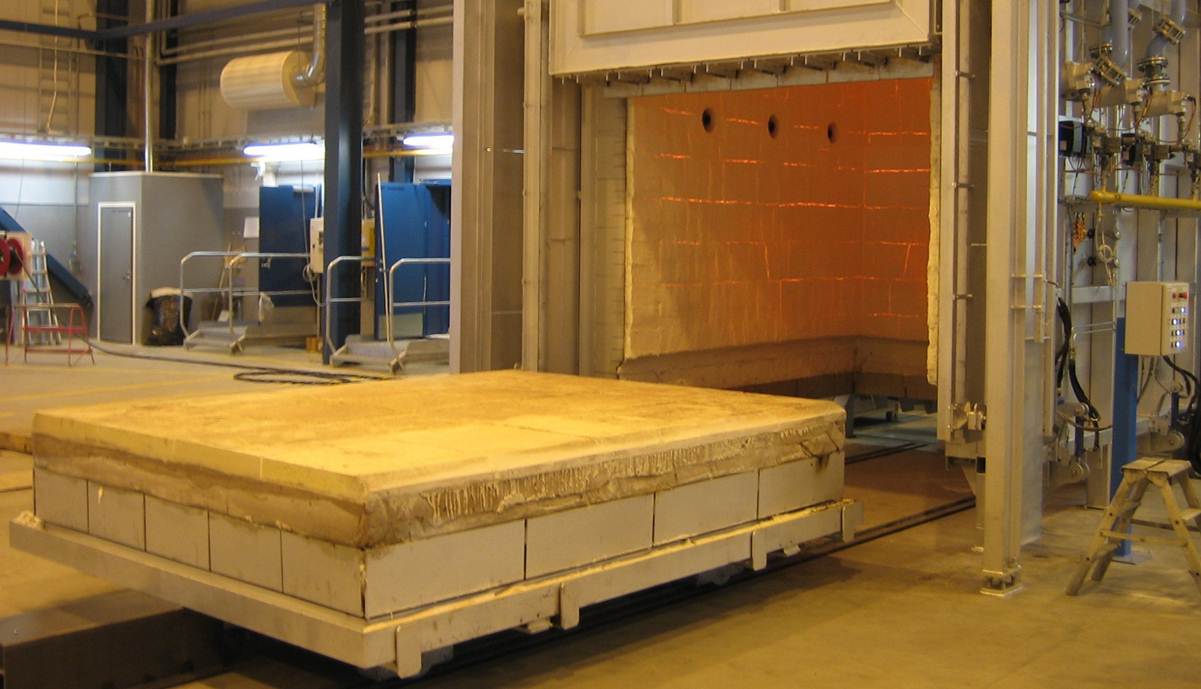
Roller kilns are increasingly used for heating processes in the ceramics and metal industry because they have a very favourable energy balance. The efficiency of roller kilns could be increased considerably by wider kiln shafts. The heat losses at the feed-throughs for the transport rollers and the lateral insulation would remain constant, while the firing throughput could be increased approximately proportionally to the width. However, the present inner dimensions are already at the limit of the mechanical load capacity of the transport rollers.
 Fraunhofer ISC, Center for High Temperature Materials and Design HTL, Bayreuth
Fraunhofer ISC, Center for High Temperature Materials and Design HTL, Bayreuth