Completed funded project
Motivation
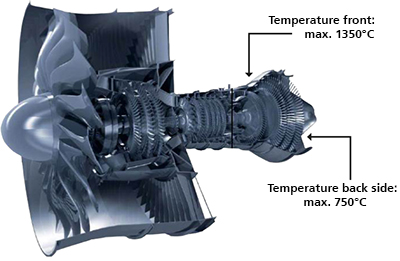
Fibre-reinforced ceramics (Ceramic Matrix Composites, CMC) have the potential to replace nickel-based alloy components in the low-pressure turbine section of an aircraft engine (e.g. outer air seals, casing structures, stators). Due to the significantly lower density of fibre-reinforced ceramics compared to nickel-based materials, a weight reduction of up to 60% can be achieved by substituting metallic components with CMC materials.
Objective
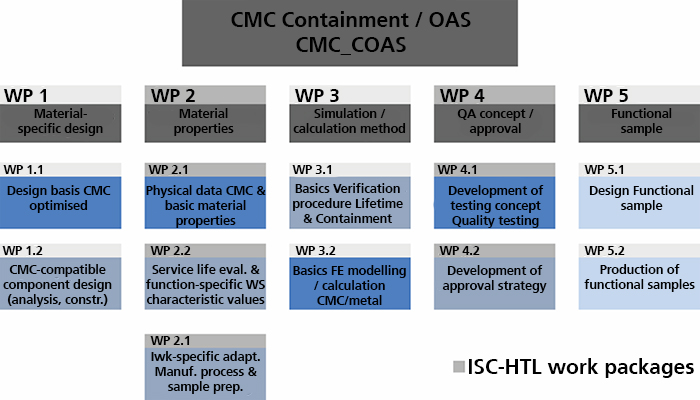
In the project, material characteristics, service life properties and lightweight construction concepts of commercial oxidic and non-oxidic CMC materials were to be determined specifically for the design of engine components. For a future aviation certification of fibre-reinforced ceramics, the basis for a quality assurance concept as well as for a certification strategy was developed.
Results
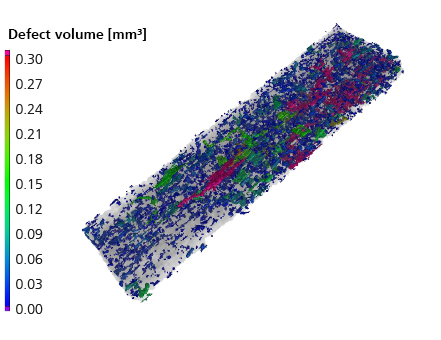
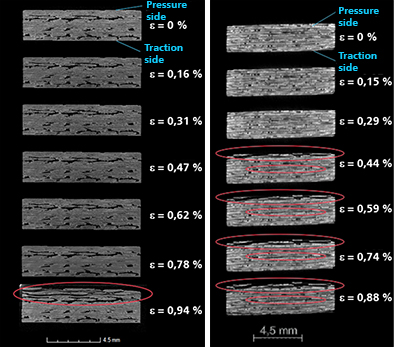
Commercially available ceramic composite materials (CMC) were evaluated in defined fields of properties with a view to subsequent aerospace certification. Both oxide ceramic composites from DLR Cologne and Pritzkow Spezialkeramik as well as silicon carbide fibre-reinforced silicon carbide (SiC/SiC) from MT Aerospace and SGL Carbon were evaluated using destructive and non-destructive testing methods. Similarly, methods for the aerospace-specific testing of CMC as well as concepts for quality testing and quality assurance were developed. Within the scope of the aviation-specific evaluation of commercial CMCs, extensive material characteristics were determined and linked in the form of a database. The determination of characteristic values was concentrated on the following areas:
- Determination of mechanical parameters of CMC materials at room temperature under static and dynamic load (fatigue tests up to 20 million load cycles)
- Determination of thermal and mechanical parameters of CMC materials in the high temperature range up to 1000°
- Investigation of the effects of enginge-specific environmental influences on the material properties
Project Data
| Project Duration | 01.10.2012 - 31.03.2016 |
| Sponsor |
Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology |
| Funding Amount | 500,000 Euro |
| Project Partners | Fraunhofer-Centre HTL MTU Aero Engines AG German Aerospace Centre MT Aerospace AG SGL Carbon SE |
| Project Coordination | MTU Aero Engines AG |
| Project Management at the HTL | Christian Eckardt |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 Fraunhofer ISC, Center for High Temperature Materials and Design HTL, Bayreuth
Fraunhofer ISC, Center for High Temperature Materials and Design HTL, Bayreuth